|
International Standards Adopted by ITU-T to Address Soft Errors Affecting Telecommunication Equipment
- Enhancing reliability based on Recommendations for design, testing, and quality estimation of measures designed to mitigate soft errors caused by cosmic rays -
TOKYO, Nov 23, 2018 - (JCN Newswire) - ITU-T, which is a United Nations specialized agency, approved standards about soft errors(1) affecting telecommunication equipment on November 13, 2018. These standards stipulate the design, testing and quality estimation methods and reliability requirements concerning measures designed to mitigate malfunctions (soft errors) in telecommunication equipment on the ground chiefly caused by cosmic rays.
 | | Figure 1: Mechanism of soft error occurrence |
 | | Figure 2: Overview of soft error Recommendations |
To develop these standards, NTT, Fujitsu, Hitachi, NEC, and Oki jointly developed draft Recommendations at "the Ad Hoc Committee on Soft Error Testing (SOET_Adhoc)" formed by TTC, and have driven efforts at ITU-T SG5(2) meetings, with the cooperation of Orange, to have these drafts adopted by ITU-T.
The adopted standards will help to establish networks that are more highly reliable based on the requirements governing measures against soft errors.
Background
In recent years, the number of soft errors caused by cosmic radiation neutrons has been increasing gradually even in telecommunication equipment located on the ground (Figure 1). The soft error disappears as soon as the semiconductor device concerned is restarted or the data concerned are overwritten. Even though a soft error in data can cause a malfunction or system outage, it is difficult to reproduce such a transient error and identify the cause. Since a soft error can have a serious impact on the user, it is a major headache for system operators. Telecommunication equipment is designed so that such malfunctions do not affect network services. However, because soft errors are difficult to reproduce, they were not sufficiently verified at the development stage.
Recently, however, it has become possible to measure the influence of soft errors on telecommunication equipment using a compact accelerator-driven neutron source(3). This measurement makes it possible to determine the influence of soft errors and take preventive measures in advance before vendors sell products and telecommunication carriers introduce telecommunication equipment into operating networks. While it has become possible for carriers to improve network quality dramatically by mitigating soft errors at the stages of equipment development and introduction, there is a need for requirements that serve as the benchmark for methods and evaluation of countermeasure.
http://www.acnnewswire.com/topimg/Low_FujitsuITUTFig1.jpg
Figure 1: Mechanism of soft error occurrence
Recommendations for soft errors in ITU-T
Against this background, at the October 2015 meeting of ITU-T SG5, commencement of a study program on soft errors in telecommunication equipment was approved with the intention of defining requirements on measures against soft errors, ranging from design to evaluation and quality. The SOET_Adhoc member companies worked together and developed draft Recommendations. ITU-T has now approved these Recommendations.
The Recommendations stipulate the design, testing and quality estimation methods and reliability requirements concerning soft errors. They include benchmarks based on which vendors and carriers can select measures against soft errors that are appropriate for the required reliability level.
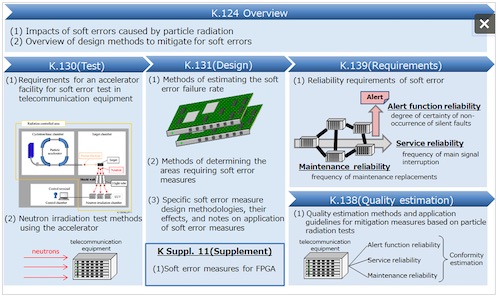
The soft-error-related standards approved by ITU-T consist of five Recommendations and a supplement. Figure 2 shows an overview of the Recommendations.
http://www.acnnewswire.com/topimg/Low_FujitsuITUTFig2.jpg
Figure 2: Overview of soft error Recommendations
Each Recommendation or supplement defines the following items:
K.124 (Overview) Overview of particle radiation effects(4) on telecommunication systems
(1) Impacts of soft errors caused by particle radiation.
(2) Overview of design methods to mitigate the impacts of soft errors.
K.130 (Test) Neutron irradiation test methods for telecommunication equipment
(1) Requirements for the accelerator facility used to test soft errors in telecommunication equipment
(2) Neutron irradiation test methods that use an accelerator
K.131 (Design) Design methodologies for telecommunication systems applying soft error measures
(1) Methods of estimating the soft error failure rate depending on the devices used and equipment configuration.
(2) Methods of determining the areas requiring soft error measures.
(3) Specific soft error measure design methodologies, their effects, and notes on application of soft error measures.
K Suppl. 11 (Supplement) Soft error measures of field programmable gate arrays
(1) Soft error measure examples for field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs).
K.139 (Requirements) Reliability requirements for telecommunication systems affected by particle radiation
(1) Definitions of standards concerning the frequency of maintenance replacements and the frequency of main signal interruption, and the degree of certainty of non-occurrence of silent faults, due to soft errors.
K.138 (Quality estimation) Quality estimation methods and application guidelines for mitigation measures based on particle radiation tests
(1) Method of determining whether various reliability requirements for telecommunication equipment regarding software defined in K.139 (Requirements) are satisfied or not, based on the results of the neutron irradiation test described in K.130 (Test).
It is expected that widespread deployment of telecommunication equipment that satisfies the requirements defined in these Recommendations will improve the reliability of telecommunication services.
(1) Soft error
Unlike a hard error, which is a fault that causes permanent malfunctioning of a semiconductor device, a soft error is a temporary error that disappears as soon as the semiconductor device concerned is restarted or the data concerned are overwritten.
(2) ITU-T SG5
ITU-T(International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Sector) is an ITU organization that issues Recommendations with a view to standardizing telecommunications.
Study Group 5 (SG5) investigates issues related to the environment and climate change.
(3) Accelerator-driven neutron source
A facility for producing neutrons through a nuclear reaction caused by irradiating the target with protons or electrons that are sped up by an accelerator.
(4) Particle radiation effects
Impact of particle radiation (emitted energy in the form of neutrons, alpha particles, etc.) on semiconductors. In recent years, the number of soft errors in semiconductors caused by neutrons generated in the atmosphere by cosmic rays has been increasing on the ground.
Contact:NEC
Seiichiro Toda
s-toda@cj.jp.nec.com
+81-3-3798-6511
Hitachi Ltd
Corporate Communications
Tel: +81-3-3258-1111
Source: Hitachi, Ltd.
Sectors: Telecoms, 5G
Copyright ©2024 JCN Newswire. All rights reserved. A division of Japan Corporate News Network. |
Latest Release

Mazda Production and Sales Results for March 2024 and for April 2023 through March 2024
Apr 25, 2024 18:21 JST
| 
MHI Begins Operation of SOEC Test Module the Next-Generation High-Efficiency Hydrogen Production Technology at Takasago Hydrogen Park
Apr 25, 2024 17:45 JST
| 
GAC Honda to Begin Sales of All-new e:NP2, the Second Model of e:N Series
Apr 25, 2024 16:50 JST
| 
Toyota Exhibiting at Beijing Motor Show 2024
Apr 25, 2024 16:25 JST
| 
Honda Reaches Basic Agreement with Asahi Kasei on Collaboration for Production of Battery Separators for Automotive Batteries in Canada
Apr 25, 2024 11:10 JST
| 
UNIQLO Sponsors KAWS + Warhol Exhibition Tour, Starting in Pittsburgh
Apr 25, 2024 09:00 JST
| 
Mitsubishi Power Begins Commercial Operation of Seventh M701JAC Gas Turbine in Thailand GTCC Project; Achieves 75,000 AOH To-Date
Apr 24, 2024 17:19 JST
| 
MC and Denka Sign J/V Agreement in Fullerene Business
Apr 24, 2024 17:02 JST
| 
Mitsubishi Motors Posts Record Sales in the Philippines in FY2023
Apr 24, 2024 13:56 JST
| 
NEC Develops High-speed Generative AI Large Language Models (LLM) with World-class Performance
Apr 24, 2024 13:25 JST
| 
Fujitsu SX Survey reveals key success factors for sustainability
Apr 23, 2024 10:25 JST
| 
Fujitsu and METRON collaborate to drive ESG success: slashing energy costs, boosting productivity with new manufacturing industry solutions
Apr 22, 2024 16:09 JST
| 
NEC Strengthens Commitment to Space Industry with Investment in Seraphim Space Venture Fund II
Apr 22, 2024 15:09 JST
| 
Soft Space Launches the First and Only JCB Payment Gateway in Malaysia
Apr 22, 2024 15:00 JST
| 
TOYOTA GAZOO Racing takes a one-two in Croatian thriller
Apr 22, 2024 10:47 JST
| 
First-ever Mazda CX-80 Crossover SUV Unveiled in Europe
Apr 19, 2024 13:50 JST
| 
Fujitsu develops technology to convert corporate digital identity credentials, enabling participation of non-European companies in European data spaces
Apr 19, 2024 10:17 JST
| 
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and NGK to Jointly Develop Hydrogen Purification System from Ammonia Cracking Gas
Apr 18, 2024 17:01 JST
| 
Toyota Launches All-New Land Cruiser "250" Series in Japan
Apr 18, 2024 13:39 JST
| 
Fujitsu and Oracle collaborate to deliver sovereign cloud and AI capabilities in Japan
Apr 18, 2024 11:14 JST
|
More Latest Release >>
|