|
Fujitsu Develops Blockchain-based Exchange System for Electricity Consumers
Contributes to stable electricity supply through energy control in peak periods
TOKYO, Jan 30, 2019 - (JCN Newswire) - Fujitsu Limited and Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. have applied blockchain technology to develop a system for trading related to energy shortages and surpluses among electricity consumers, including factories and retail stores.
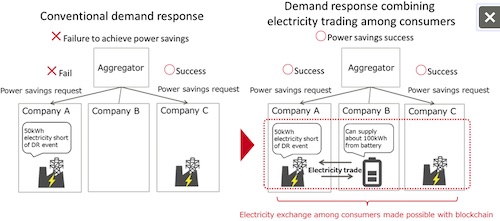 | | Figure 1: Image of consumers exchanging electricity in demand response |
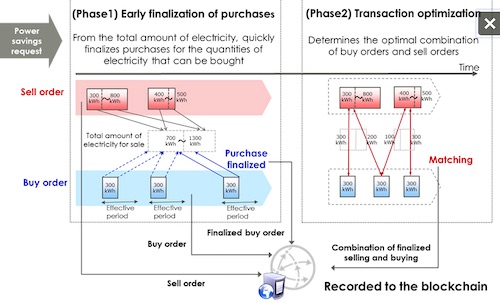 | | Figure 2: Outline of technologies for electricity exchange transactions among consumers |
Demand response (DR) is a scheme in which electric utilities and consumers of electricity cooperate to control the amount of electricity used during periods of expected peak demand. An issue, however, is that the success rate for DR controls can be low, with consumers being unable to meet the amount of power savings requested by electric utilities.
Fujitsu has now devised a system in which electricity consumers can efficiently exchange among themselves the electricity surpluses they have produced through their own electricity generation or power savings. The company then applied blockchain, and with the cooperation of ENERES Co., Ltd., the system was used in a simulation using the actual data of electricity consumption. The result was an approximately 40% improvement to the DR success rate.
Improvement to the DR control success rate is expected to lead to more consumers participating in DR schemes. Moreover, this will enable the stable supply of electricity and the expansion of renewable energy use, another goal of the DR scheme. Fujitsu Limited and Fujitsu Laboratories will carry out further system verification and strive to build a carbon-free society.
Details of the new technology will be showcased at the ENEX 2019 Energy and Environment Exhibition, being held from Wednesday, January 30, to Friday, February 1, at Tokyo Big Sight.
Development Background
Demand response has been in the spotlight as renewable energies and other initiatives are being put in place to develop a carbon-free society. DR, in which electric utilities and electricity consumers cooperate to control the amount of electricity use, aims to reduce electricity consumption, particularly at peak times when shortages of electricity supply are expected, by paying compensation to electricity consumers who contributed to power savings.
In practice, DR is arranged so that an aggregator, who receives the request for power savings from the electric utility and controls the amount of each consumer's power savings, acts as the middleman, and assigns amount of the consumer's power savings. When the amount of power savings requested is achieved, the aggregator receives remuneration from the electric utility.
The aggregator also distributes the remuneration to contributing consumers based on the amount of the power savings they achieved. However, consumers are sometimes unable to meet request from the aggregator, due to shortages in the electricity produced when they operate their own generator or due to sudden spikes in their energy consumption, so there are cases of consumers being unable to receive compensation.
In order to realize a carbon-free society, it is important to increase the success rate of DR, which indicates the ratio of consumers who are compensated for achieving their power savings targets. It is also essential to secure an investment effect when consumers have joined the DR scheme and to increase the number of participants.
Issues
At present, the aggregator interacts with individual consumers on a one-to-one basis to allot power savings amounts and to confirm whether the request can be acceptable for the consumer. For electricity consumers to achieve their power savings targets with a high probability, it can be expected that an exchange that allows a consumer who is short of meeting its targets to quickly exchange a portion of another consumer's power savings amount would be effective. This approach, however, has yet to be applied to DR.
Fig 1: Image of consumers exchanging electricity in demand response
http://www.acnnewswire.com/topimg/Low_FujitsuBlockchainFig1.jpg
Developed Technology
Fujitsu Laboratories has applied blockchain technologies it has developed to create a system of exchange in which electricity consumers who have contracted with an aggregator can exchange amounts of power saving among consumers.
With DR, it is sometimes necessary to quickly respond to the aggregator about whether power savings can be achieved. As depicted in figure 2, Fujitsu Laboratories has developed a technology that first calculates the total amount of electricity that can be offered from the sell orders registered on the exchange system, and determines which buy orders can be settled quickly, in turn, for the quantities that can be purchased. As a result, the technology makes it possible to quickly reply about whether power savings targets can be met. The company also developed a technology that optimizes pairing exchange orders, so that, after the response, required sell orders are distributed to the completed buy orders without waste.
This two phased electricity exchange technology (patent pending) is built on blockchain, which guarantees the transparency of recorded exchange transaction results. This enables the accurate distribution of remuneration based on the transaction results of finalized selling and buying-the amount of power savings. With this exchange system, even when the requested amount of power savings is difficult to achieved, a consumer can quickly purchase the surplus electricity of another consumer to supplement its own power savings goals, leading to more reliable achievement of the targets.
Fig 2: Outline of technologies for electricity exchange transactions among consumers
http://www.acnnewswire.com/topimg/Low_FujitsuBlockchainFig2.jpg
Effects
With the cooperation of ENERES, Fujitsu conducted simulations of the new system in the two terms of 2018, summer and winter. Using the actual logs of energy consumption of 20 consumer sites, the companies observed the situation in which electricity consumers could exchange electricity among themselves. As a result, the company confirmed a maximum improvement to the DR success rate of about 40%, compared to conventional methods. By supporting the advancement and popularization of DR with this system, Fujitsu will contribute to the creation of carbon-free society.
Future Plans
Fujitsu is a member of the RE100, which aims to have companies use 100% renewable energy for the electricity they consume, and is putting measures in place to build a carbon-free society. As part of these efforts, the company is carrying out verification of this system in a real-world environment, with the goal of commercialization from fiscal 2019.
About Fujitsu Laboratories
Founded in 1968 as a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujitsu Limited, Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. is one of the premier research centers in the world. With a global network of laboratories in Japan, China, the United States and Europe, the organization conducts a wide range of basic and applied research in the areas of Next-generation Services, Computer Servers, Networks, Electronic Devices and Advanced Materials. Please see: http://www.fujitsu.com/jp/group/labs/en/.
Contact:Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.
Security Research Laboratory
E-mail: fjbcdr-ir@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
Fujitsu Limited
Public and Investor Relations
Tel: +81-3-3215-5259
URL: www.fujitsu.com/global/news/contacts/
Source: Fujitsu Ltd
Sectors: Cloud & Enterprise, Energy, Alternatives, Alternative Energy
Copyright ©2025 JCN Newswire. All rights reserved. A division of Japan Corporate News Network. |
Latest Release

Fujitsu to develop ETF trading platform based on TSE's CONNEQTOR and provide it to Australian Securities Exchange
Jul 03, 2025 11:14 JST
| 
Mitsubishi Motors Launches the All-New Grandis for the European Market
Jul 02, 2025 12:10 JST
| 
Valuufy partners with Mainichi Future Creation Lab, Supporting New Approaches to Business Sustainability
Jul 02, 2025 12:00 JST
| 
Fujitsu launches solution to enhance customers' global supply chain resilience
Jul 02, 2025 11:32 JST
| 
MHI Receives Order to Supply Four Circulating Water Pumps for Units 5 and 6 of Sanmen Nuclear Power Plant in China Under Collaboration with Dongfang Electric Machinery
Jul 02, 2025 11:30 JST
| 
Multi-purpose Arena in Odaiba Aomi Area TOYOTA ARENA TOKYO Construction Completed
Jul 01, 2025 22:56 JST
| 
1Finity, a Fujitsu company, commences operations and reveals brand identity
Jul 01, 2025 22:53 JST
| 
MHI Thermal Systems Begins Field Test of Jointly Developed "Surplus Renewable Energy Absorption and Release System"
Jul 01, 2025 22:40 JST
| 
Japan's Telecommunications Carriers Strengthen Disaster Response Through Collaborative Information Sharing
Jul 01, 2025 22:30 JST
| 
JCB and Mandai Wildlife Group Deepen Partnership with exclusive discounts for JCB cardmembers
Jul 01, 2025 16:00 JST
| 
Fujitsu provides Japan's first AI-powered cloud-based library search service
Jul 01, 2025 11:30 JST
| 
JCB Brings Apple Pay to Cardmembers in Vietnam
Jul 01, 2025 11:15 JST
| 
First Shipment of LNG from the LNG Canada Project
Jul 01, 2025 11:00 JST
| 
Approval in Principle (AiP) for World's First LCO2 / Methanol Carrier
Jun 30, 2025 20:30 JST
| 
Acropolis Rally Greece: Day 4 Sunday success and second overall for TOYOTA GAZOO Racing's Ogier
Jun 30, 2025 20:15 JST
| 
Mitsubishi Fuso-Hino Merger: 4 Firms Collaborate for the Future of Commercial Vehicles
Jun 30, 2025 20:10 JST
| 
Six Companies Establish BlueRebirth Council to Expand Use of Recycled Materials in New Vehicles
Jun 30, 2025 19:25 JST
| 
Honda Changes Plan to Build New Production Plant for Next-generation Fuel Cell Module in Japan
Jun 30, 2025 19:20 JST
| 
MHI-AC&R Receives Recommendation Award of JARAC's 42nd Excellent Energy Saving Equipment Awards
Jun 30, 2025 19:00 JST
| 
The University of Osaka and Fujitsu Japan launch joint research on AI-powered education support for culturally and linguistically diverse children in Japan
Jun 30, 2025 12:00 JST
|
More Latest Release >>
|